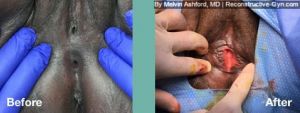
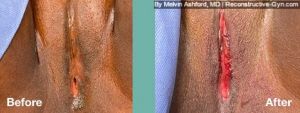
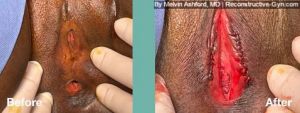
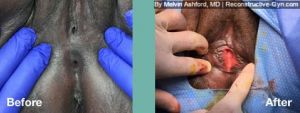
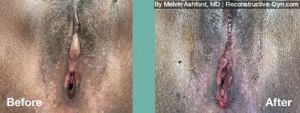
FGM (Female Genital Mutilation) or Female Circumcision is a practice common to parts of Africa, the Middle East, and Southeast Asia. During this procedure, normal, healthy genital tissue is removed or altered on young girls before puberty.
Possible Long-Term Complications from FGM
- Recurrent bladder infections
- Cysts
- Infertility
- Higher rate of childbirth complications
About FGM (Female Genital Mutilation)
and FGM Reversal
What is FGM?
Female Genital Mutilation (FGM) or Female Circumcision is a destructive procedure performed on girls before puberty. The procedure, often referred to at the “cut,” is performed in some parts of Africa, the Middle East, and Southeast Asia. Reports of it occurring in the USA and European Countries in immigrant communities have been reported as well.
About FGM
During the procedure, the female genitals are partly or entirely removed or sewn with the goal of controlling a woman’s sexual feelings. The procedure is usually performed on girls before puberty without an anesthetic using crude instrumentation. The procedure can leave women with genital anatomy that makes sex difficult or painful. Also, it may make delivering a baby more difficult.
Women also can have lifelong emotional scars as well as pelvic pain. Difficulty with urination can occur as well as potential HIV or infection from instruments that were not properly sterilized.
Help for Women with FGM
Respectful anatomic restoration is offered here. We offer therapy to address the resultant pelvic pain and anatomic defects of FGM.
Treatment of FGM is geared to toward addressing symptoms and restoration of anatomy. The surgical restoration of anatomy is dependent upon they type of FGM procedure that was initially performed. The most common types are classified as: